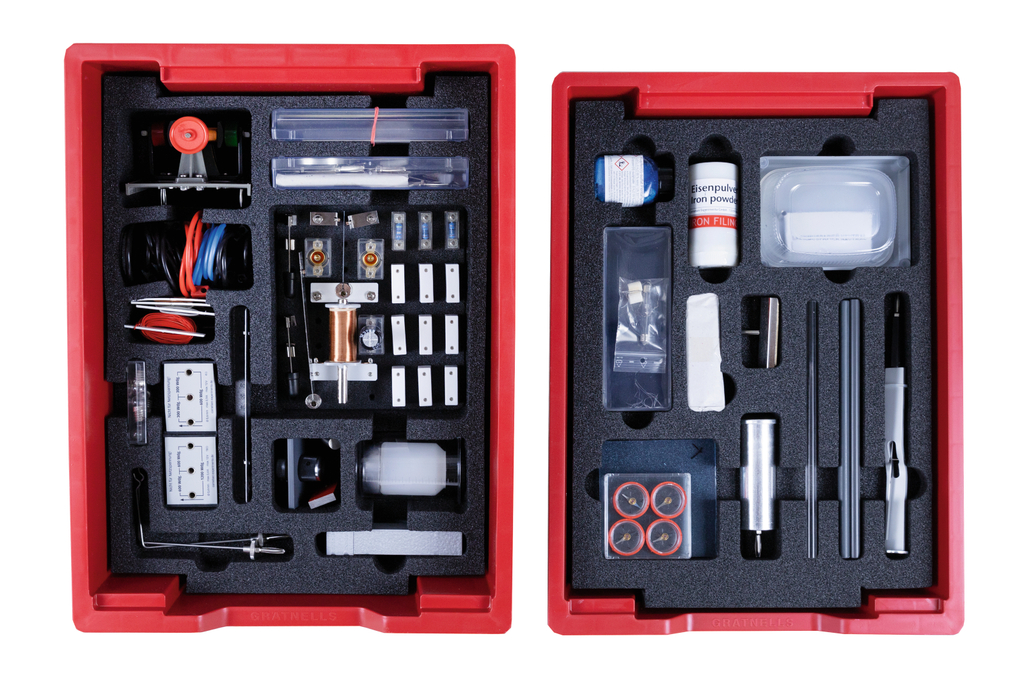
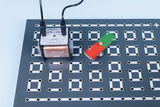
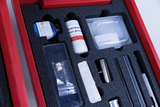
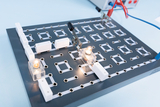
Students kit Electricity including circuit board
The kit contains equipment and resources required for investigating the basic laws of electrical processes.
To meet the demands of and applications in different types of schools this science kit consists of three modules:
Experiments on current flow and on the electrical basic circuits, Art. No. 23210
- Experiments on the effects of electric current and examinations of selected engineering usage
- The components of the basic unit are stored in a plastic tray.
Electricity – upgrade induction and alternating current, Art. No. 23220
- Continuing experiments on electromagnetism and on electromagnetic induction The supplement can be stored in the tray of the basic unit electricity 1.
Electricity – upgrade electrostatics, magnetism and electrochemistry, Art. No. 23230
- Examinations to demonstrate the properties of permanent magnets Experiments to demonstrate electrical charge and how charges behave
- Experiments to demonstrate the basics of electrochemistry
The components of this supplement are stored in a separate tray.
This kit covers the following basic laws of physics:
- Coulomb’s law
- Faraday's law of induction
- Ohm’s law
- Oersted’s law
- Galvanic cell
- Lenz´s law
The experiment shows the relationships between the quantities U=voltage, I=current and R=resistance.
The experiment shows to what extent a parallel connection or a series connection influences the electrical output.
In this experiment, the heat development of a current-carrying heating wire is observed.
The experiment deals with the structure of a circuit, with a bimetallic switch, and its influence on the circuit.
In this experiment, the effect of the relay is observed.
An induction current is always directed in such a way that it counteracts the origin of the creation.
This experiment explains the principle of a transformer.
A transformer can increase or decrease charges and resistances.
The students build a pendulum from pieces of elderberry pulp and examine the electrical state.
The experiment shows the effect of a pendulum piece with an electrically charged plastic rod.
The magnetic field is a special state of space in which electrically charged bodies are attracted or repelled.
The students build an electrical circuit.
Students build an electrical circuit with a switch.
Test to determine the conductivity of different substances.
Students examine the power line of various liquids.
In the experiment, it is observed what differences there are in the voltage when one or more incandescent lamps are switched on.
This experiment shows the effect of resistance on the current and the lamp associated with it.
This experiment shows the effect of resistance on the current and the lamp associated with it.
It is investigated what difference there is when connecting several incandescent lamps in a row and what effects this has on the current.
In this experiment, the series connection of resistors is investigated.
In this experiment, the parallel connection of incandescent lamps is investigated and what effect this has on the circuit.
The experiment investigates the effect of resistors, in a parallel connection, on the current.
The experiment shows the effect of an adjustable resistance on an incandescent lamp.
In this experiment it is observed what effect it has on a lamp when the voltage changes.
This experiment is for measuring specific resistances of different materials.
This experiment examines the conductivity of a wire when it is cold and when it is heated.
In this experiment, the system of a bridge circuit and its effect on the voltage of an incandescent lamp will be explained to you.
In this experiment, the resistance measurement is examined using an ammeter.
This experiment illustrates how electrical energy is converted into thermal energy.
This experiment shows how electrical energy is converted into light, like an incandescent lamp.
In this experiment, the difference between a power and a resistance wire is examined.
The experiment shows how a fuse works and makes sense in a circuit.
In this experiment, the position of a hooked weight is observed, which is suspended from a current-carrying conductor. From the observations, conclusions are drawn about the change in the position of the hook weight.
In this experiment, the effect of the magnetic field of a conductor is observed.
This experiment shows the effect of an electromagnet and is compared with that of a permanent magnet.
This experiment shows the structure of a self-interrupter, how it works and what processes take place in it.
This experiment illustrates the principle of an electric motor and how it works.
By applying a voltage to the electric motor, you get a rotary movement.
Here, electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy.
This experiment shows the inductance of a coil.
Induction is the movement of land carriers in a conductor.
This experiment examines the inductance of a coil in a DC circuit.
This experiment illustrates the principle of self-induction of a coil.
Self-induction is the ability of a coil to generate a voltage in a changing magnetic field.
This experiment illustrates how a generator works and how it works.
The alternator is used to generate single-phase alternating current.
An AC motor runs on single-phase AC power.
It is also called an induction motor.
In this experiment, the difference in the resistance of a coil with DC voltage and AC voltage is measured.
This experiment illustrates the charging and discharging processes of a capacitor.
This experiment shows the change in resistance of a capacitor in DC and AC circuits.
Static electricity or friction is a type of charge separation. This creates a charge difference on the different bodies.
This experiment shows how charged bodies behave when approaching.
The experiment shows the change in the electroscope when its electrode is touched with an electrically charged plastic rod.
The experiment shows the effects when the charged plastic rod approaches the uncharged plastic rod.
The experiment shows the influence on the electroscope.
The experiment examines the electrical state when a charged plastic rod touches a metal cup and a glow lamp inside the metal cup.
In this experiment, the magnetic properties of different metals are tested.
The force of magnets means that like poles attract and different poles repel.
Magnetic influence refers to the magnetization of ferromagnetic materials. This happens when they come into a magnetic field strong enough to align their elemental magnets.
The way a compass works means that the needle always points to the geographic north pole, which is the same as the physical south pole. Therefore, it can be said that the earth is a great magnet.
Electrolysis is used to break down chemical elements under the influence of an electric current.
In this experiment, the influence of a copper sulphate solution when an electrical voltage is applied is examined.
In this experiment, the chemical processes occurring when the electrodes are immersed in the acidic electrolyte are observed.
In this experiment, the chemical processes are observed using different substances when the electrodes are immersed in the acidic electrolyte.
- 1 ×
- 1 × ||Students kit Electricity modules - Basics including circuit board
- 1 × Students Kit Electricity - Upgrade Induction and Alternating Current (AC)
- 1 × Students Kit Electricity - Upgrade Electrostatics, Magnetism and Electrochemistry