Physics experiments on magnetism
Station experiments from the basics to para- and diamagnetism
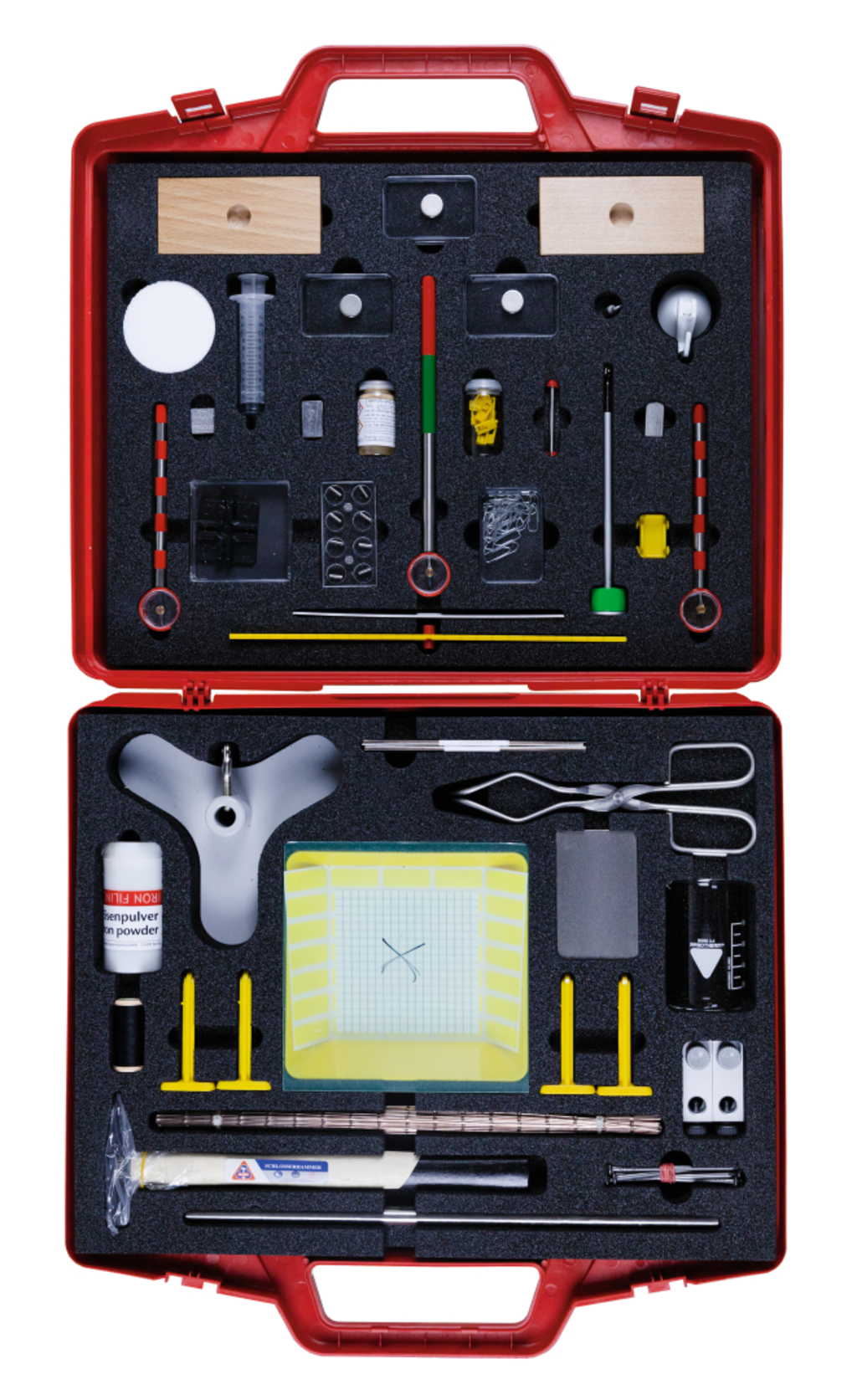
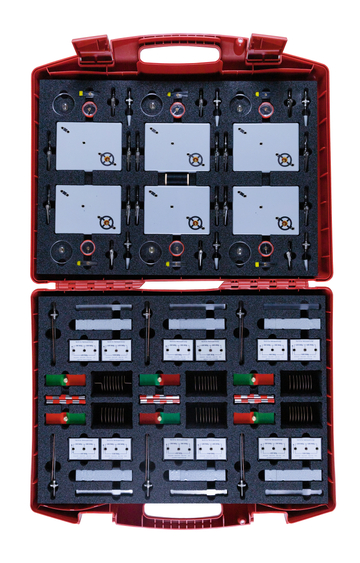
In 14 different stations your whole class can explore the elementary properties of magnetism as well as novel experiments in the field of dia- and paramagnetism. With the included checklist for students, all experimental results can be directly recorded and evaluated.
All topics in one case:
- Elementary properties and interaction of magnets
- Magnetic properties of materials in everyday life
- Explaining magnetic phenomena with models
- NEW: Diamagnetism and paramagnetism (e.g. Moses effect)
- Properties of magnetic fields
- The Earth’s magnetic field and the compass
Special equipment:
Neodymium magnets for the exploration of dia- and paramagnetism (see picture below)
Magnetic field model to demonstrate the properties of magnets (see picture above right)
The students each use two small bar magnets to investigate the attraction and repulsion of permanent magnets of comparable strength. To do this, the small bar magnets are brought closer to each other in the four possible orientations.
The students discover that iron attracts the magnet as well as the magnet attracts the iron and thus open up the principle of interaction.
The students examine the strength of the magnetic force at different points along a large bar magnet.
The students examine the material properties of metals and everyday materials. To do this, they use a small bar magnet and first observe the magnetic force acting on the five specified metal strips made of iron, aluminum, copper, nickel and zinc by observing whether these objects stick to the magnet.
The students use a strong neodymium magnet to discover the paramagnetic and diamagnetic properties of aluminum and graphite.
The station first demonstrates that diamagnetic and paramagnetic forces also act on liquids.
The students analyze the magnetic material properties of aluminum and graphite and compare the diamagnetic and paramagnetic forces quantitatively.
According to the station card, the students magnetize a nail using a small bar magnet and demagnetize it by shaking and heating it.
The station copies the experimental procedure from Station 8, replacing the nail to be painted over with the model of microscopic compass needles. In this way, the students should be able to understand the microscopic effect of the macroscopic activity of magnetizing and demagnetizing.
The students examine the magnetic properties of partial magnets using an iron wire that can be broken into individual parts.
The magnetic field of a long bar magnet is studied using iron filings.
The students examine which materials can be used to shield a magnetic field.
The students first deal with the earth and the four cardinal points in the workbook and then build a swimming compass.
In order to practice dealing with coordinates, a timeline on the history of magnetism is made in the check booklet at this station.
- 1 × Set labels, yellow
- 2 × Tubular clip, 5x4 mm
- 1 × Screen, transparent, 150x150 mm
- 1 × Glass, empty
- 1 × Carton for storage box, 481x425x107
- 2 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 2 ×
- 2 ×
- 1 ×
- 2 ×
- 3 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 3 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 10 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 3 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 1 ×
- 10 × Magnet rod, AlNiCo, 23 mmwith red-marked northpole
- 1 × Sewing thread, 100 m
- 1 × Paper clips (100 pcs.)
- 4 × Plastic box, clear, 60/40
- 1 × Cross base
- 1 × Tripod stand, 80 mm
- 1 × Magnet rod Alcomax 75x10
- 4 × Stand for small magnets
- 1 × Tacks for magnet mounting(100 pcs.)
- 2 × Bosshead with slit
- 1 × Mass hanger, 1 g
- 1 × Mass hanger, 10 g
- 1 × Slotted mass, 50 g, green
- 1 × Lever with bores
- 1 × Floating disc, styrofoam,60 mmØ f.magnetic rod
- 2 × Dish, plastic, yellow 150x140x35mm
- 1 × Magnet rod, AlNiCo red/ green, 100 x 10 mmØ
- 1 × Iron wires w. notches pack of 100 pcs.
- 1 × °Sifter with iron powder
- 1 × Metal axis 50 mm
- 1 × Crucible tongs, stainless
- 1 × Plastic box, smooth 64x64x15 mm
- 1 × Storage box, red 430x330x99 mm
- 2 ×
- 1 ×